A LEVEL: Philosophy and Ethics, Life after Death (Edexcel)
Philosophy & Ethics
Life after Death
Why as humans are we so obsessed with the idea of life after death?
- We are scared of death
- Hard to accept that we only have one short shot at life
- Moral law is only fulfilled when the god are rewarded and evil are punished, but this doesn't always happen so there must be another way to achieve this: Life after Death.
- There could be more to human potential
- It is gift from God
Arguments against the concept of an after life
- Death is part of a biological function and a necessary part of the natural process
(when we die so does our personality and consciousness)
- Notion of life after death is a meaningless dicuscciod because we have no empirical evidence of life after death : A.J.Ayer, logical positivism
- Life after death is a contradiction as the two are two exclusive states.
- Dawkins poses the questions of why we require religion in order to find a meaning in life, when ‘We are so grotesquely lucky to be here’.
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
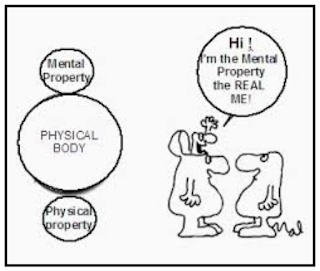
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE BODY AND THE SOUL
For those who believe in a life after death, the most important question is what survives after death, is tit the body or the spiritual?
To understand this point of view, we first need to define what the differences are between the mind and the body.
monistic: the mind & body are one
dualistic: the mind & body are two distinct entities, but can influence each other
1. The mind depends on the body in order to function.
2. Mind and body influence each other equally, but both need each other in order to be conscious and active in the world.
3. Body and mind are two distinct entities that have been locked together, but the soul can escape the body to find life after death.
Religious Interpretation: Each person has an individual soul possibly created by God.
THE MONISTIC VIEW: psycho-physical unities.
The physical body: talks, walks, sleeps and so on
The mind: determines mental behaviour, personality and qualities such as intelligence and humour.
‘Man does not have a body, he is a body … he is flesh-animated-by-soul, the whole conceived as a psycho-physical unity’ - J.A.T.Robinson
Gilbert Ryle: ‘ghost in a machine’ (Ghost = mind, Machine = body) Ryle introduced the idea of philosophical behaviourism - (all events that seem mental are really physical we just perceive them as mental)Therefore, when we speak of the body and mind being separate entities we are contradicting ourselves, because they rely on each other in order to exist. He was a monistic believer.
THE DUALISTIC VIEW: physical body and the spiritual soul are regarded as distinct entities.
Descartes said that the body may be spatial but it was not capable of conscious thoughts, and therefore could not be a part of one whole union between the body and the mind. The mind is not spatial and is capable of conscious thoughts.
He thought the very act that we were able to doubt ourselves was proof of two distinct entities within us, cogito ergo sum, even if we can’t doubt the body we can doubt the mind and therefore there must be a separate mind and body.
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
Two areas which have been looked at in order to ascertain there being the possibility of life after death.
- Near Death Experiences
- Parapsychology
Philosopher: Gilbert Ryle
The soul and mind are the SAME
He mentioned the ‘ghost in a machine’
He advocated philosophical behaviourism.
All mental events are physical events which have been interpreted in a mental capacity.
Therefore, it is a category akin. And a separation, within a category. The University can be separated from its buildings but it is still a university. Subcategorisation.
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
Near Death Experiences:
When someone dies for a short while then comes back to life.
Raymond Moody: many similarities between patients or people who had experienced NDEs.
- daydreaming
- the loss of subconscious memory
- hallucinations caused by lack of oxygen in the brain
K.Ring: NDEs are unique to the individual but there are similar ‘core experiences’
- out of body experiences
- a feeling of peace
- seeing the light
Peter Fenwick: he went on to identify certain characteristics of NDEs
Feelings of peace:
morphine can induce NDEs/
or the release of endorphins as a coping mechanism to deal with the fear of death.
or ACTH (adrenaline) which helps cope with stress
cannot be tested so not a satisfactory explanation.
Out of Body experiences:
if the mind can exist without the brain (duality) then it is possible
could have been induced by psychedelic drugs/psychologically induced
somethings are possible even when lying on the table rather than out of body
The tunnel and the light
light = metaphor for divine realities
The Being of Light
described as a positive loving feeling
interpreted religiously usually
figure is said to hold great authority
The Barrier
visitors cannot pass this barrier
interpreted that NDEs are a spiritual journey that our life is regulated by providence and providence has decreed that it is not yet our time to die.
Another Country
Often described as a idyllic pastoral scene, full of light and beauty
symbolic of a place like heaven? or is the patient just trying to reassure themselves subconsciously?
Relatives and friends
seeing relatives that have passed away
reassurance in that death is not scary, but can be comforting
Life Review
sometimes occurs in front of the being of light
some people feel judged, told what tasks to do and accept - hence return back to the living world
could be the result of anoxia: the temporal lobe becomes excited due to the lack of oxygen and causes random firing and excitation.
but then why are the memories so clear?
interpretations could be that they see it as a forecast of the life review after death
The decision to return
Some people want to stay in this ball of fluff where the experience can continue on, but once the decision is made to return, they have to deal with it.
anoxia explanation: sudden return of oxygen is a shock to the system
religious explanation: the divine providence is like yo your spiritual energy is done and go back wooah
The Return
rapid and the victim does not fear death anymore
drastic change in lifestyle
victim becomes serene and compassionate, sometimes self righteous
may believe in God more, if not already
receive gifts (mehu)
Raymond Moody: The evidence only raises more questions than answers.
‘How do we decide if they are hallucinatory or genuinely spiritual?’
Susan Blackmore: hoopla a woman yaas
- Explanation must be coherent & specific - no generalities, but particular features
- Should not over exaggerate the case and point fingers at supernatural beings, assumptions
- Theory must have testable predictions
Swinburne: principle of credulity
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
Parapsychology
The study of the spiritual realm.
Spiritualist movement is suffering, as their is damage to credibility.
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
Reincarnation
Is also known as the transmigration of souls, or rebirth in another body.
Claim: Reincarnated bodies remember their past lives or memories, and may show bodily marks from previous lives.
Does the soul affect the body or does the soul affect the actual physical body.
KARMA is the principle of cause and effect.
all acts or deeds leave a long term imprint on a future transmigration of the actor.
(Hinduism) Life and death is considered part of this cycle of existence. This cycle goes on till the soul achieves Nirvana and is united with Brahman. All souls seek for coexistence with Brahman.
- Soul’s Journey is governed by Karma
- The reincarnation is determined by how good or bad their karma was.
The soul is in a state of illusion:
- sthula sharira, ‘the gross body’, the physical vessel
- linga sharira, ’the subtle body’, the mind or soul
Hick: ‘the subtle body may accordingly be characterised as a psychic organism consisting of a structure of mental dispositions but differing from ‘person’ in that it lacks self consciousness.’
Soul is not reincarnated only on earth, but only the physical earthly realm allows the soul to achieve nirvana, as the soul has the freedom to be able to make choices and decisions where it can discover the path to enlightenment and perfection.
- On reincarnation, body is temporary and dies
- If we cannot remember our previous lives then our memory is lost too
- So only the psychological pattern of personal character remains.
Evidence for Reincarnation:
Dr Ian Stevenson:
- Investigated cases in which people say they have memories of past lives and where some who knew the person in that life can collaborate these memories.
- Birthmarks, to substantiate claims, but failing to do so.
- All cases happen in societies where reincarnation is accepted as a reality
- Long time gap between cases, so improbable that story was made up
- language difficulties, so the interpreters may have had some biases
All this offers is a vague unconscious thread of memory linking all the past lives together. We can say that people are similar but not that they are the same.
Hick proposed eschatological verification.
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
Rebirth
Is a buddhist concept and slightly different to hinduism although the two share similarities.
- Anatta (no soul)
- Anicca (temporary)
- Dukkha (suffering)
The body is made up of the physical body and four mental elements (feeling, perception, moral will and consciousness) - called the nama-rupa. At death the physical body dies and the nama-rupa is released and the character aspects of the previous are installed into the new person. Rebirth does not have to be back to earth. The temporal soul wants to achieve nirvana.
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
Resurrection
- Promise of post-death existence in a recreated human body. Monist theory, a physical body is required for redemption
- Dualist theory if the soul is separated from the body to await a final resurrection on judgement day.
Traditionally…
… bodily resurrection occurs when Jesus returns at the end of time
… Soul is immediately reunited with God
- Bible scriptures of Jesus’ Resurrection
St.Paul
- argued in favour for resurrection
- if Jesus was resurrected then humans can also hope for the same to occur
- if God is omnipotent then he should be able to create a perfect body for the resurrection
- St.Paul
▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂
IMMORTALITY OF THE SOUL
Plato:
Dualist: Mind and body are two different entities that are in conflict within each other. Although the body is physical it lusts for materialism rather than for knowledge, truth and beauty the latter three are sought after by the metaphysical soul or mind. As a result of this,
Rene Descartes: He was also sceptical of the physical world and so relied presently on the soul, and the thinking mind which he saw as the metaphysical. It was the only way in which humans could understand the after life.
Immanuel Kant: He stated that life’s goal is to achieve summum bonum or the greatest and best good, if humans cannot achieve this before they die then surely God would not waste human potential. Life after death is a way in which human can achieve summum bonum.
Against:
Heaven: Problematic, unclear theory based on scriptures that have no credible base apart form historical. What actually is Heaven, and what do we know about it? Described as a place of God yet




Comments
Post a Comment